Setting up DMARC
How does DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) work?
DKIM is based on the use of a key pair consisting of a private and a public key, similar to asymmetric encryption.
Sending DKIM-protected emails
Firstly, a hash value is calculated for each outgoing email based on the SHA-256 algorithm from the content of the email and parts of the header. SHA1 has become obsolete as an encryption algorithm and may no longer be used according to RFC 8301. The header fields used to calculate the hash must be specified in the DKIM signature. A hash value is nothing more than a long string of characters.
The sending server now uses the private key to sign the calculated hash value using the RSA method or the Ed25519 method and adds this signed hash value to the email header as a signature.
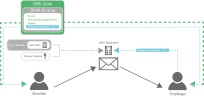
Receiving DKIM-protected emails
The sender has previously stored their public key together with other information as a DKIM entry in the Domain Name System (DNS) of their domains. This allows the recipient of the respective email to check the signature and the hash value.
More precisely, the receiving server of a DKIM-protected email first determines the sender domain of the email by reading its 'Header-From' field. There he also finds the so-called selector. The selector specifies the name under which the matching public key can be found in the DNS zone of the sender domain.
If the hash value check fails, either the public key is incorrect or the email has been changed en route.
The DKIM signature therefore ensures two things:
-
The receiving server knows that the email and its content have not been changed in transit.
-
The receiving server knows that the owner of the sender domain specified in the header is actually the sender.
What does a DKIM entry look like?
With DKIM, the sender creates a TXT record in the DNS zone of the domain to be protected - as with SPF - on the basis of an RFC-standardised syntax. The DKIM entry consists of the following elements:
Version Frequently specified by the expression v=DKIM1.
Encryption algorithm used Either k=rsa or k=Ed25519.
Selector A freely selectable character string. A consecutive number or a date is usually selected.
Public key p=YourPublicKey.
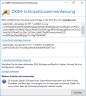
Example of a DKIM key
-
Upper box: DKIM entry with public RSA key.
-
Bottom box: DKIM entry with public Ed25519 key.
See also
Setting up SPF
Sender reputation and email security - Part 3: DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) (blog article)